
The Wheel of Emotions: A Guide to Basic Human Feelings

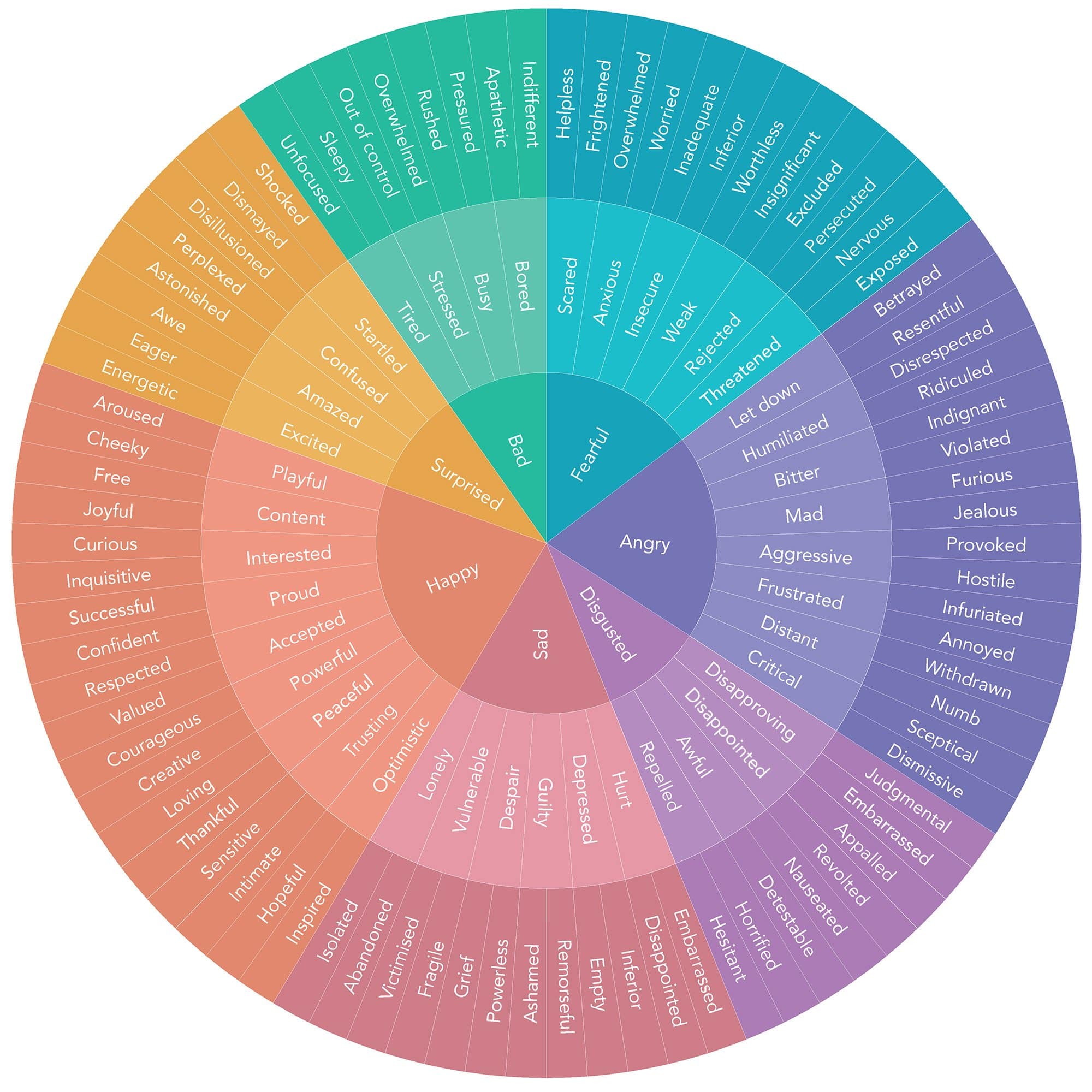
Dr. Robert Plutchik’s research reveals that humans can experience 34,000 distinct emotions, which emerge from eight primary feelings. People can better understand their complex emotional experiences through the wheel of emotions, a valuable psychological tool.
Human emotions play a vital role in psychological health and personal development. Research by psychologist Paul Ekman shows five core emotions – joy, sadness, fear, disgust, and anger. These emotions appear universally in all cultures through distinct facial expressions. Dr. Gloria Willcox’s Feelings Wheel offers a well-laid-out method to identify emotions through primary, secondary, and tertiary layers.
This piece examines the psychological foundations of human emotions and their biological markers. It also shows practical ways to develop stronger emotional awareness in everyday life.
The Science Behind Basic Human Emotions
The human emotional system started as a vital survival mechanism [1]. Simple reflexes grew into complex neural networks that help humans adapt quickly to changing situations.
Evolutionary Purpose of Core Emotions
Core emotions helped humans survive by letting them:
Find food and shelter
Choose suitable mates
Protect offspring
Escape dangerous situations
Build social bonds
Neurological Basis of Emotional Processing
The brain’s emotional processing works through a complex network of structures. The amygdala acts as the central hub to process negative emotions like fear and anger [1]. The hippocampus-based network combines different types of memory with emotional processing [2]. The anterior cingulate cortex links emotional responses to decision-making processes.
Role of Brain Chemistry in Emotional Responses
Brain chemistry arranges emotional experiences through essential neurotransmitters:
Neurotransmitter | Primary Role in Emotions |
|---|---|
Controls mood stability and emotional well-being [3] | |
Dopamine | Creates feelings of pleasure and satisfaction [3] |
Norepinephrine | Triggers fight-or-flight responses [1] |
These chemical messengers work together to create an array of human emotional experiences. Different brain regions and neurotransmitters interact to produce subtle emotional responses that define human behavior. Humans can experience a wider range of emotional states than other species because of this sophisticated system [4].
Understanding the 5 Core Emotions
Scientists discovered 40 years ago that human emotions work on two distinct levels. Primary emotions appear as instant, gut reactions to stimuli, especially when quick reactions matter [5]. These original feelings transform into secondary emotions that your personal experiences and cultural background shape.
Primary vs Secondary Emotions
The main difference between primary and secondary emotions shows up in their timing and complexity. Primary emotions serve as direct reactions to events, especially when you need an immediate response [6]. This relationship becomes clear in the following table:
Primary Emotions | Secondary Emotions |
|---|---|
Immediate reactions | Learned responses |
Universal across cultures | Culturally influenced |
Instinctual | Cognitively processed |
Short duration | Longer lasting |
Universal Emotional Expressions
Facial expressions work as a universal language of emotion. Notwithstanding that, people from different cultures notice these expressions in their own way [7]. Research shows that East Asian participants rely mostly on the eyes to read emotions. Western observers focus on both eyebrows and mouth instead [7].
Cultural Variations in Emotional Display
Culture substantially changes emotional expression through:
Display rules that control appropriate emotional demonstrations [8]
Variations in emotional arousal levels between Eastern and Western cultures [9]
Different cultural values regarding emotional intensity [9]
Western cultures typically value high-arousal emotions. Eastern cultures prefer low-arousal emotional states [9]. These cultural differences shape how people express their emotions and influence their emotional experiences [10].
Mapping Emotions on the Psychology Emotion Wheel
The psychology emotion wheel helps us map and understand human feelings better. Psychologist Robert Plutchik created this visual tool that shows eight basic emotions arranged like flower petals [11].
Structure and Organization of the Wheel
There are several different variations of the emotion wheel, some with 5 base emotions, others with 6, 7or 8. It isn’t so important that you use any one wheel, what’s more important is being able to identify nuances in emotional feelings so that you can understand what you are feeling and process it properly.
Intensity Levels and Gradients
Color gradients show how intense each emotion is as you move up and down the wheel [13]. Emotions get stronger toward the center, shown by darker shades. To cite an instance, see how:
Anger grows from annoyance to rage
Joy builds from serenity to ecstasy
Fear rises from apprehension to terror [11]
Emotional Combinations and Blends
The spaces between primary emotions show how feelings mix to create more complex emotional states [11]. When basic emotions combine, they create secondary emotions like:
Primary Emotions | Combined Result |
|---|---|
Joy + Trust | Love |
Trust + Fear | Submission |
Anticipation + Joy | Optimism |
Sadness + Disgust | Remorse [14] |
This organized approach helps people identify and understand their feelings more clearly [15]. The wheel works as a practical tool that builds emotional literacy and shows how different feelings connect and change over time [13].
Biological Markers of Different Emotions
Emotions show themselves through distinct biological markers in our bodies. The autonomic nervous system coordinates these responses and creates unique patterns for different emotional states [16].
Physiological Changes During Emotional States
Our bodies react to emotions through measurable physical changes. Research shows that skin conductance level, heart rate, and blood volume pulse are reliable indicators during emotional states [16]. Scientists analyzed these responses and found:
Emotion | Primary Physiological Response |
|---|---|
Fear | Increased heart rate and blood pressure [17] |
Anger | Surge in adrenaline, muscle tension [17] |
Sadness | Decreased heart rate, slower breathing [17] |
Joy | Reduced blood pressure, muscle relaxation [17] |
Facial Expression Patterns
Facial expressions communicate emotions universally, but their interpretation differs between cultures. Research shows East Asian observers mostly focus on the eyes, while Western observers look at both eyebrows and mouth to interpret emotions [18]. The Facial Action Coding System identifies 21 distinct emotion categories through specific muscle movements [18].
Body Language Indicators
Body language powerfully communicates emotional states. Research has shown that:
People recognize anger better by watching hand movements [19]
The trunk’s movements are key indicators of sadness [19]
Overall body posture helps detect happiness [19]
Body language provides more accurate emotional information than facial expressions alone [20]. People’s bodily expressions become especially important in conveying genuine feelings during intense emotional experiences [20].
Developing Emotional Awareness
Better emotional awareness starts when you understand how feelings shape behavior and affect daily interactions. Note that emotional awareness creates a foundation for better self-understanding and interpersonal relationships [21].
Recognizing Emotional Triggers
Physical and psychological responses demonstrate emotional triggers. Research shows that triggers can activate fight, flight, or freeze responses, which lead to:
Pounding heart and upset stomach
Shakiness or dizziness
Sweaty palms and physical tension [2]
Understanding Personal Response Patterns
Deep-rooted experiences and learned behaviors create personal response patterns. A study shows emotional patterns connect directly to past experiences and create reactive responses regardless of their appropriateness to current situations [21]. Mindful observation helps you identify recurring emotional patterns and modify your responses.
Response Level | Characteristics | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Body sensations | Immediate reaction |
Mental | Thought patterns | Interpretation |
Behavioral | Action tendencies | Long-term habits |
Building Emotional Vocabulary
A broader emotional vocabulary equips you to express feelings with greater precision. Research shows reflection plays an essential role in processing vital experiences [21]. Regular emotional awareness exercises help people:
Label observed feelings accurately
Verify emotional experiences
Model appropriate emotional expression [22]
Building emotional awareness needs consistent practice and patience. A feelings journal helps track emotional patterns and identify specific triggers that affect daily interactions [2].
Practical Applications of the Emotion Wheel
The psychology emotion wheel serves as a powerful tool to help people grow personally and professionally. Studies show that people who use emotion wheels develop better emotional literacy and communication skills [23].
Using the Wheel for Self-reflection
People can track their emotional patterns over time through the wheel of emotions. Most people tend to use vague words like “fine” or “upset,” but the wheel gives them a structure to pinpoint specific feelings [23]. The key practices of self-reflection are:
Daily emotion tracking
Pattern identification
Trigger recognition
Response analysis
Emotional Communication Strategies
People can express their emotions more clearly in different settings with the core emotions wheel. A well-laid-out approach to emotional communication has:
Setting | Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Personal | Precise emotion naming | Reduces misunderstandings |
Professional | Boundary setting | Improves workplace dynamics |
Therapeutic | Pattern recognition | Helps treatment planning |
Decision-making with Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence plays a vital role in making better decisions in professional settings. Leaders who show high emotional intelligence achieve better financial results in their companies [24]. The most important aspects of emotionally intelligent decision-making are:
Recognizing emotional triggers
Understanding what impacts team members
Providing clear explanations for choices
Standing firm with commitment
The wheel helps people identify layered emotions—like feeling excited yet anxious before big events—which leads to more nuanced decision-making [23].
Managing Complex Emotional States
Self-regulation is a key skill you need to manage complex emotional states. It helps you control your behaviors, thoughts, and impulses while keeping your emotions stable [1].
Techniques for Emotional Regulation
The Stop-Breathe-Reflect-Choose approach is the quickest way to regulate emotions [1]. This process has these steps:
Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Stop | Pause reaction | Prevent impulsive responses |
Breathe | Take deep breaths | Activate calming system |
Reflect | Think about options | Assess consequences |
Choose | Select response | Make mindful decisions |
Dealing with Mixed Emotions
Life changes and big decisions often bring mixed emotions [3]. You don’t need to eliminate these feelings – just accept them. Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) has showed great results when people manage emotional conflicts. It helps them learn about the mechanisms while improving their overall well-being [3].
Transforming Negative Emotions
Challenging emotions need a balanced approach to transform. Research shows negative emotions can spark positive change through:
Finding issues that need attention
Driving behavioral changes
Pointing to needed life adjustments
Creating growth opportunities
Cognitive behavioral strategies reduce emotional dysregulation by replacing unhelpful thoughts with positive ones [1]. Mindfulness practices help you enjoy simple pleasures and build resilience against stress [1].
Integrating Emotional Intelligence in Daily Life
People who integrate emotional intelligence into their daily lives see measurable benefits in all areas. Studies show emotional intelligence makes up 58% of job responsibilities, and all but one of these top performers show high emotional quotients [25].
Workplace Emotional Management
Both individual and team performance depend on emotional competence in professional settings. A well-laid-out approach to workplace emotional management has these components:
EQ Component | Workplace Benefit |
|---|---|
Self-awareness | Better decision-making |
Empathy | Improved team dynamics |
Regulation | Improved conflict resolution |
Social skills | Stronger leadership |
Emotional Intelligence in Relationships
Couples with strong emotional intelligence build lasting and deeper connections [26]. Their relationships benefit from:
Clear communication of thoughts and needs
Better ways to handle conflicts
Mutual support and understanding
Healthy boundary setting
Personal Growth Through Emotional Awareness
Emotional awareness creates lasting changes in behavior. People with high emotional intelligence show greater resilience when facing challenges [27]. This growth shows through:
Better self-understanding
Better stress management
Improved decision-making abilities
Stronger connections with others
Emotional intelligence helps people recognize when they need breaks, identify stress triggers, and set proper boundaries [28]. Regular practice leads to clearer emotional understanding that helps people choose their responses instead of reacting on impulse.
Conclusion
Emotional understanding and management are the life-blood of psychological well-being and personal growth. The wheel of emotions is a powerful framework that helps people identify and process their feelings precisely.
Scientific research shows how emotions come from complex neurological processes that brain chemistry and evolution shape. These basic emotional responses show through specific biological markers, facial expressions, and body language patterns that exceed cultural boundaries.
Emotional intelligence tools reshape personal and professional relationships. People who become skilled at emotional awareness make better decisions, build stronger connections, and show higher resilience against challenges. Their improved self-understanding helps them guide complex emotional states.
People need consistent practice and dedication to develop emotional intelligence. Regular self-reflection, a broader emotional vocabulary, and mindful observation help them learn about their emotional patterns. This knowledge enables them to choose thoughtful responses instead of acting on impulse.
The trip toward emotional mastery grows as science reveals new discoveries about human feelings and their effect on behavior. These psychological tools and understanding help people build meaningful relationships and lead more satisfying lives.
FAQs
Q1. What are the five core emotions according to psychologists? The five core emotions identified by psychologists are joy, sadness, fear, disgust, and anger. These emotions are universally recognized across cultures through distinct facial expressions.
Q2. How does the wheel of emotions help in understanding feelings? The wheel of emotions, developed by psychologist Robert Plutchik, organizes eight primary emotions in a flower-like structure. It helps individuals identify and understand their emotional experiences with greater precision by showing how different feelings relate to one another and evolve over time.
Q3. Can emotions be physically measured? Yes, emotions can be physically measured through biological markers. Skin conductance level, heart rate, and blood volume pulse demonstrate excellent reliability during emotional states. Different emotions trigger distinct physiological responses, such as increased heart rate for fear or reduced blood pressure for joy.
Q4. How can I improve my emotional awareness? You can improve your emotional awareness by recognizing emotional triggers, understanding personal response patterns, and building an emotional vocabulary. Keeping a feelings journal, practicing mindful observation, and regularly reflecting on your emotions can help track patterns and identify specific triggers that influence daily interactions.
Q5. What role does emotional intelligence play in the workplace? Emotional intelligence plays a significant role in the workplace, accounting for 58% of job responsibilities. It contributes to better decision-making, enhanced team dynamics, improved conflict resolution, and stronger leadership. Individuals with high emotional intelligence often demonstrate better performance and are more likely to be top performers in their roles.
References
[1] – https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/self-regulation-for-adults-strategies-for-getting-a-handle-on-emotions-and-behavior
[2] – https://www.healthline.com/health/mental-health/emotional-triggers
[3] – https://www.betterhelp.com/advice/relations/a-guide-to-conflicting-feelings-dealing-with-mixed-emotions/
[4] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2723854/
[5] – https://www.simplypsychology.org/primary-and-secondary-emotions.html
[6] – https://www.betterhelp.com/advice/general/what-are-primary-and-secondary-emotions/
[7] – https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2011/09/facial-expressions
[8] – https://www.paulekman.com/resources/universal-facial-expressions/
[9] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5381435/
[10] – https://www.paulekman.com/blog/cultural-differences-in-emotional-expressions/
[11] – https://www.betterup.com/blog/emotion-wheel
[12] – https://positivepsychology.com/emotion-wheel/
[13] – https://www.6seconds.org/2022/03/13/plutchik-wheel-emotions/
[14] – https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-an-emotion-wheel-6500040
[15] – https://www.berkeleywellbeing.com/emotion-wheel.html
[16] – https://jphysiolanthropol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40101-019-0209-y
[17] – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381311629_Physiological_Changes_Associated_with_Emotions
[18] – https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1322355111
[19] – https://www.in-mind.org/article/how-body-language-helps-us-understand-other-peoples-emotions
[20] – https://www.princeton.edu/news/2013/01/15/dont-read-my-lips-body-language-trumps-face-conveying-intense-emotions
[21] – https://psychologyfanatic.com/emotional-patterns/
[22] – https://www.elchc.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Emotional-Vocabulary-Wheel-Worksheet.pdf
[23] – https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/commit/202411/the-emotion-wheel
[24] – https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbescoachescouncil/2019/05/24/four-elements-of-making-emotionally-intelligent-decisions-in-the-workplace/
[25] – https://insights.vitalworklife.com/emotional-intelligence-what-is-it-and-why-its-important-in-daily-life
[26] – https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/making-love-last-importance-of-emotional-intelligence-0601184/
[27] – https://managementconcepts.com/resource/how-emotional-intelligence-helps-your-professional-growth/
[28] – https://blog.heartmanity.com/how-to-improve-emotional-intelligence-in-everyday-life-and-relationships
